How Does A Dry Well Septic System Work
Understanding the Inner Workings of a Dry Well Septic System
A dry well septic system is an alternative method for managing wastewater in areas where traditional septic systems are not feasible. This innovative system offers an efficient and environmentally friendly way to dispose of household wastewater. In this blog post, we will explore how a dry well septic system works, highlighting its key components and processes.
The Basics of a Dry Well Septic System
A dry well septic system, also known as a cesspool or soakaway pit, relies on the natural filtration capabilities of the soil to treat and disperse wastewater. Instead of utilizing a traditional septic tank and drain field, a dry well system directly infiltrates wastewater into the ground, promoting the percolation and natural purification of the effluent.
The Components of a Dry Well System
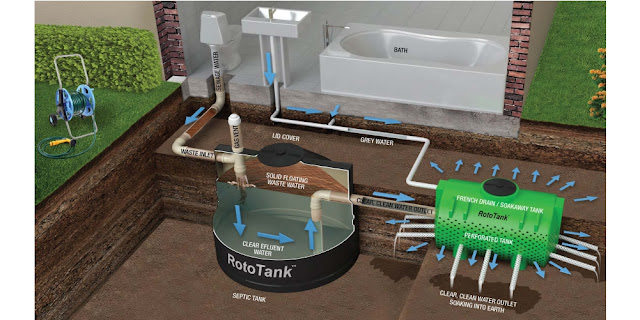
A dry well septic system consists of several key components that work together to effectively manage wastewater. These include:
a. Inlet Pipe: The wastewater from the household plumbing system enters the dry well system through the inlet pipe.
b. Dry Well: The dry well, typically constructed using concrete rings or perforated plastic, acts as a reservoir for the wastewater. It allows for the temporary storage and gradual infiltration of the effluent into the surrounding soil.
c. Gravel Bed: Surrounding the dry well is a layer of gravel that serves as a filter medium. It prevents soil particles from clogging the dry well and facilitates proper drainage.
d. Soil: The soil surrounding the dry well plays a crucial role in treating and dispersing the wastewater. It acts as a natural filter, removing contaminants and allowing for the percolation of treated effluent.
e. Ventilation Pipe: A ventilation pipe, equipped with a vent cap, ensures the proper release of gases that may accumulate within the dry well.
The Wastewater Treatment Process
The wastewater treatment process in a dry well septic system involves several stages:
a. Collection: Wastewater generated from sinks, toilets, showers, and other household sources is directed into the dry well system through the inlet pipe.
b. Sedimentation: Once inside the dry well, the effluent undergoes sedimentation. Heavy solids and particles settle at the bottom, forming a layer of sludge.
c. Filtration: As the wastewater percolates through the gravel bed, it undergoes natural filtration. The gravel layer filters out further impurities, helping to clarify the effluent.
d. Biological Breakdown: Soil microorganisms present in the surrounding soil play a vital role in the biological breakdown of organic matter and the removal of harmful pathogens.
e. Percolation: Treated effluent gradually percolates through the soil, where it undergoes additional purification through natural biological and physical processes.
f. Recharge: The treated water replenishes groundwater reserves, benefiting the local ecosystem.
Benefits and Considerations
Dry well septic systems offer several benefits, including:
a. Cost-Effectiveness: Dry wells are often more affordable to install and maintain compared to traditional septic systems.
b. Environmental Friendliness: By relying on natural filtration and treatment processes, dry well systems have minimal environmental impact and help conserve water resources.
c. Space Efficiency: Dry wells require less space than conventional septic systems, making them ideal for properties with limited land availability.
d. Versatility: Dry well systems can be designed to accommodate various soil types, allowing for implementation in diverse geographic areas.
However, it's important to consider potential limitations such as soil permeability, groundwater levels, and local regulations. Consulting with a professional septic system designer or installer can help determine the feasibility of a dry well system for your specific property.
Conclusion
A dry well septic system offers a practical alternative for wastewater management, relying on natural filtration and percolation processes. By understanding how the components work together and the treatment process involved, homeowners can make informed decisions regarding their septic system options. It is advisable to consult with experts to ensure compliance with local regulations and suitability for your property, ultimately promoting effective and environmentally friendly wastewater disposal.


Comments
Post a Comment